In times of economic uncertainty, investors often turn to gold as a safe haven. But how does gold perform against inflation in 2025? With rising prices and shifting monetary policies, understanding gold’s role as an inflation hedge is more critical than ever. In this article, we’ll explore historical trends, recent data, and expert insights to determine whether gold remains a reliable store of value.
What Is Inflation and Why Does It Matter?
Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services increases over time, eroding purchasing power. For example, if inflation is 3% annually, $100 today will only buy $97 worth of goods next year. High inflation can devastate savings, making assets like gold attractive for preserving wealth.
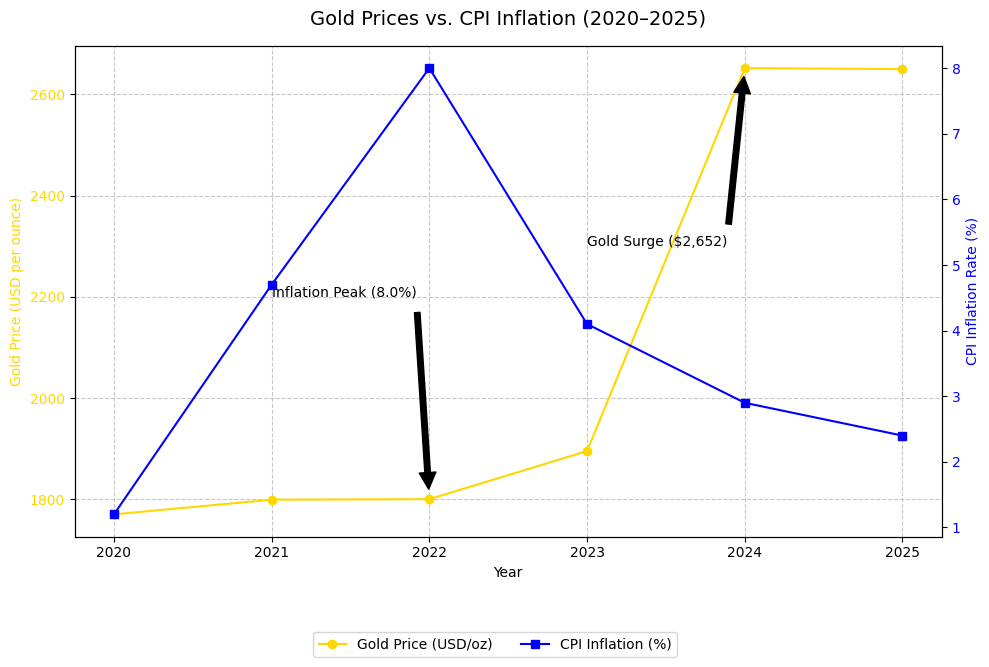
Key Statistic: According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation rate was 2.9% in March 2025, down from a peak of 9.1% in June 2022.
Understanding inflation’s impact is crucial for investors seeking assets that maintain or grow value over time.
Gold as an Inflation Hedge: The Historical Perspective
Gold has long been viewed as a hedge against inflation due to its scarcity and intrinsic value. Historically, gold prices tend to rise when inflation accelerates, as investors seek to protect their wealth.
- 1970s Stagflation: During the high-inflation era of the 1970s, gold prices soared from $35 per ounce in 1971 to $850 by 1980, a 2,300% increase, outpacing the decade’s average inflation rate of 7.1%.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: Gold prices rose from $800 in 2008 to $1,900 by 2011, driven by quantitative easing and inflation fears.
- 2020-2022 Pandemic Era: Gold hit an all-time high of $2,074 per ounce in August 2020 as inflation surged post-COVID.
Insight: Data from the World Gold Council shows gold has delivered an average annual return of 10.6% from 1971 to 2024, often outperforming inflation during turbulent periods.
How Has Gold Performed Against Inflation in 2025?
In 2025, gold’s performance has been shaped by global economic conditions, including central bank policies, geopolitical tensions, and currency fluctuations. As of April 2025, gold prices hover around $2,650 per ounce, up 15% year-to-date, according to Kitco News.
- Inflation Context: With U.S. inflation stabilizing at 2.9%, gold has outpaced CPI growth, signaling its continued relevance as an inflation hedge.
- Global Demand: Central banks, particularly in China and India, have increased gold reserves, driving demand and supporting price stability.
- Market Volatility: Geopolitical events, such as trade disputes and Middle East tensions, have bolstered gold’s safe-haven appeal.
Factors Influencing Gold’s Performance
Several factors determine how gold performs against inflation:
- Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve’s rate hikes in 2022-2023 initially pressured gold prices, as higher yields on bonds compete with non-yielding assets like gold. However, anticipated rate cuts in 2025 have supported gold’s rally.
- U.S. Dollar Strength: A stronger dollar typically suppresses gold prices, as gold is priced in USD. In 2025, a weakening dollar has boosted gold’s appeal.
- Supply and Demand: Mining output remains constrained, while demand from jewelry, technology, and investment grows.
- Geopolitical Risks: Ongoing conflicts and trade uncertainties enhance gold’s safe-haven status.
Pro Tip: Monitor the Federal Reserve’s interest rate announcements and the U.S. Dollar Index (DXY) for clues on gold price movements.
Gold vs. Other Assets: A Comparison
How does gold stack up against other inflation hedges like stocks, real estate, or cryptocurrencies?
- Stocks: Equities can outperform inflation over the long term but are volatile during economic downturns. The S&P 500 returned 8.5% annually from 1971-2024, slightly below gold’s 10.6%.
- Real Estate: Property values often rise with inflation, but real estate is illiquid and requires significant capital.
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin is often called “digital gold,” but its volatility (e.g., 50% drawdowns in 2022) makes it riskier.
- TIPS (Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities): TIPS guarantee inflation-adjusted returns but offer lower upside compared to gold.
| Asset | Annualized Return | Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| Gold | 10.6% | Moderate |
| S&P 500 | 8.5% | High |
| Real Estate | 7.2% | Low |
| Bitcoin | 30% (2010-2024) | Extreme |
Why It Matters: Gold’s moderate volatility and historical performance make it a balanced choice for investors seeking stability during inflationary periods.
Should You Invest in Gold to Combat Inflation?
Gold remains a compelling option for diversifying portfolios, but it’s not without drawbacks:
Pros
- Proven inflation hedge during crises.
- Tangible asset with global demand.
- Low correlation with stocks and bonds.
Cons
- No income generation (e.g., dividends or rent).
- Storage and insurance costs for physical gold.
- Short-term price volatility.
Investment Options
- Physical Gold: Bars, coins, or jewelry (e.g., via dealers like JM Bullion).
- Gold ETFs: SPDR Gold Shares (GLD) offer liquidity without storage hassles.
- Gold Mining Stocks: Companies like Newmont Corporation provide leveraged exposure to gold prices.
Expert Tip: Allocate 5-10% of your portfolio to gold for diversification, as recommended by financial advisors like Ray Dalio.
Conclusion: Is Gold Still a Safe Haven?
Gold’s performance against inflation in 2025 reaffirms its status as a reliable hedge, particularly during economic and geopolitical uncertainty. While it may not always outpace inflation in stable times, its long-term track record and unique characteristics make it a valuable portfolio component.
Ready to invest in gold? Research reputable dealers or ETFs, and consult a financial advisor to align your strategy with your goals.